As a homeowner, I have often wondered why are bed bugs so hard to kill? It seems like no matter how much time and effort I put into getting rid of them, they always seem to come back. This has led me to research the difficulty of killing these insects, so that I can better understand why they are such a nuisance.
What are Bed Bugs?

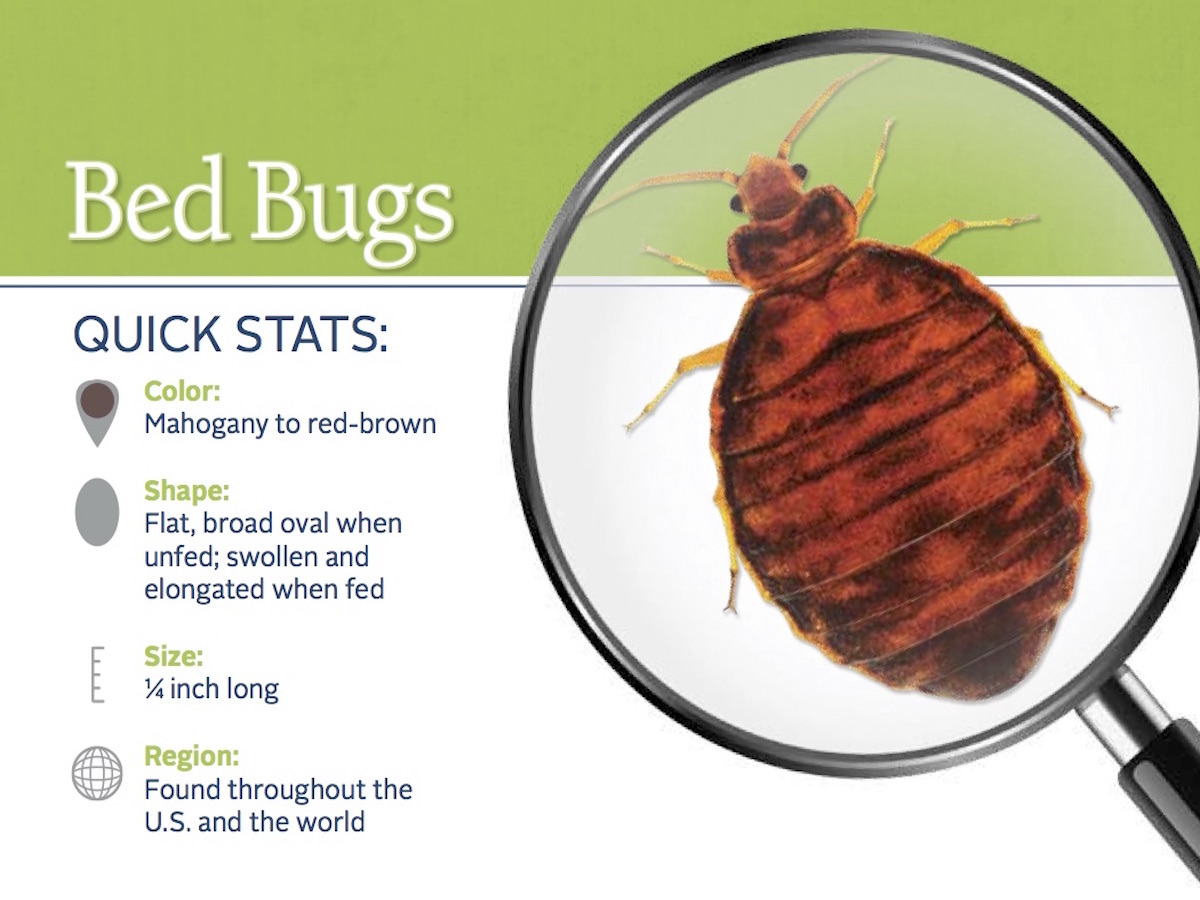
Bed bugs are small, wingless, parasitic insects that feed exclusively on the blood of humans and other warm-blooded animals. They are reddish-brown in color, about the size of an apple seed, and have a flattened, oval-shaped body. Bed bugs hide in mattresses, box springs, bed frames, and headboards; under wallpaper and carpets; and in other furniture, crevices, and cracks.
Bed bugs can:
- Live up to one year without food
- Produce up to five generations of offspring in one year
- Reproduce quickly and in large numbers
- Travel between rooms in multi-unit buildings, such as apartments and hotels
They are notorious for their resistance to insecticides, which makes them difficult to eradicate.
Characteristics of Bed Bugs

Bed bugs are resilient pests that can survive for months without feeding and can withstand temperatures from nearly freezing to 122 degrees Fahrenheit. They are also small, making them difficult to detect, and they can hide in tiny crevices and cracks. Bed bugs can also travel easily, as they can crawl up to 100 feet in a night and can be transported on clothing or in luggage. Additionally, they reproduce quickly and can lay up to 500 eggs in their lifetime. Lastly, bed bugs have become resistant to many pesticides, making them even more difficult to eradicate.
Bed Bug’s Reproduction Rate
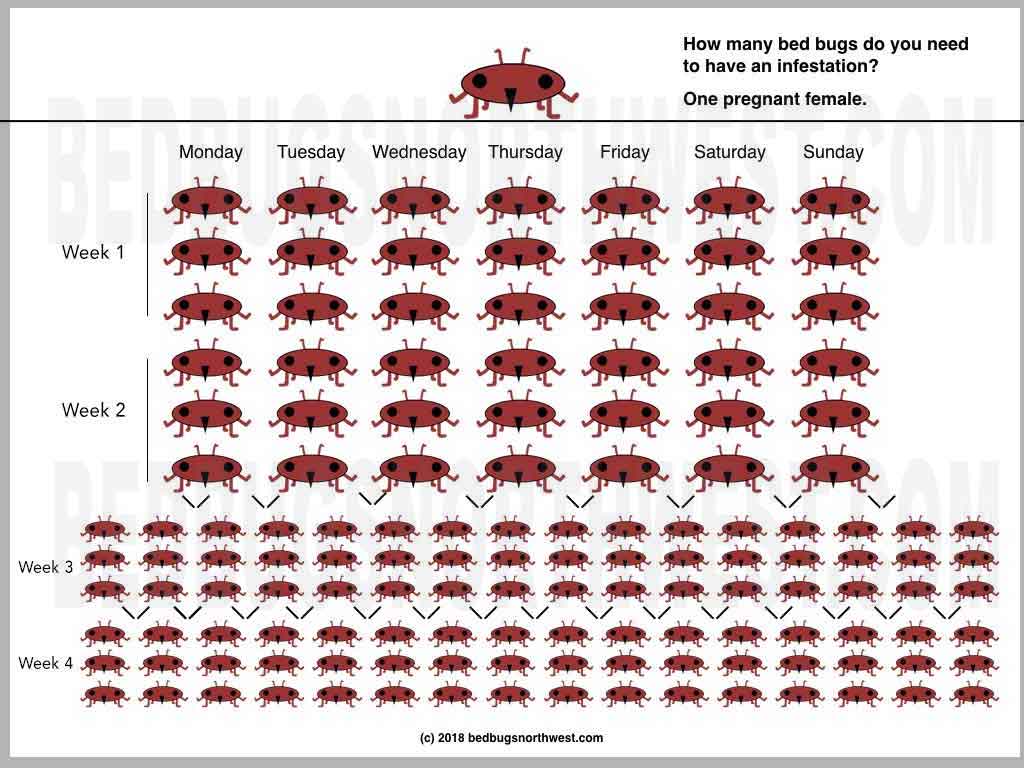
Bed bugs are incredibly hard to kill due to their rapid reproduction rate. A single female bed bug can lay up to five eggs in a single day, producing up to 500 eggs in her lifetime. This means that a single bed bug can produce an entire colony in a very short amount of time. The eggs are incredibly small, only 1mm in size and can be laid in almost any crevice. They hatch in as little as 6-10 days, meaning that a bed bug infestation can rapidly become out of control. Female bed bugs also don’t need to mate in order to reproduce, they can produce offspring asexually, meaning that it only takes one bed bug to produce an entire population.
Hiding Habits of Bed Bugs
Bed bugs are notoriously hard to kill, in large part due to their hiding habits. Bed bugs are excellent hiders and can squeeze into the tiniest of cracks and crevices, making them difficult to spot and even more difficult to exterminate. Here are some of the hiding habits of bed bugs:
- Bed bugs prefer to hide in dark, warm and humid places, such as mattresses, box springs, bed frames, headboards, baseboards, furniture, behind wallpaper and inside of electronic devices.
- They are highly mobile, and can easily move from room to room, as well as spread throughout multiple dwellings.
- They can hide in tiny cracks and crevices that are too small for a human to see or reach.
- They often hide near their food source, which is usually humans.
- They can survive for up to a year without a blood meal.
- They hide during the day and come out at night when it is dark to feed.
Understanding the hiding habits of bed bugs is essential to knowing how to effectively eliminate them. Without proper knowledge, it is nearly impossible to successfully eradicate a bed bug infestation.
Chemical Resistance of Bed Bugs

Bed bugs have evolved to resist many of the commonly used insecticides. This makes them harder to kill and can lead to re-infestation. While their resistance to insecticides varies, their ability to survive and reproduce can make them difficult to eradicate.
One way that bed bugs are resistant to chemicals is through their cuticle, or outer layer of their bodies. This cuticle protects them from insecticides and other chemicals, making it harder to penetrate their bodies and kill them. Additionally, bed bugs can also develop resistance to certain chemicals by changing their physiology.
| Chemical | Resistance |
|---|---|
| Pyrethroids | High |
| Neonicotinoids | High |
| Organophosphates | Moderate |
| Carbamates | Low |
The table above shows the resistance of bed bugs to different chemicals. Pyrethroids and Neonicotinoids have a high resistance, which makes them harder to kill. Organophosphates have a moderate resistance, while Carbamates have the lowest resistance of the four.
When attempting to kill bed bugs, it is important to use the chemical that is most effective for the particular species. This will help reduce the risk of re-infestation due to resistance. Additionally, it is important to use the chemical correctly and follow all safety procedures.
Bed Bug Detection

Bed bugs are nocturnal creatures and are typically active at night. They’re also very small which makes them difficult to spot. The most effective way to detect a bed bug infestation is to look for physical signs of them or their feces. Signs of bed bugs include dark spots on mattresses, sheets or pillowcases, or small bugs on or near the bed. Bed bug feces are dark, rust-colored stains that may appear on mattresses, bedding, walls, or other surfaces.
To confirm an infestation, you may need to use a magnifying glass and a flashlight to inspect the suspected area. You can also use a handheld vacuum to collect bugs and eggs, or use a bed bug detector. Bed bug detectors are devices that detect bed bugs by using chemical, infrared, or carbon dioxide sensors.
Table
| Detection Method | Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Visual inspection | High |
| Bed bug detector | Moderate |
| Vacuum | High |
Once you’ve identified an infestation, you need to take steps to get rid of the bed bugs. This is difficult because bed bugs can hide in hard-to-reach places, such as cracks in furniture, wall voids, baseboards, and behind electrical outlets. Insecticides can be used to kill bed bugs, but they may not be effective against all bed bug populations.
Bed Bug Control
Bed bugs are one of the most difficult pests to control. I have personally dealt with bed bugs in my own home, and I can tell you from experience that they are not easy to get rid of. Bed bug control requires a combination of prevention and extermination methods.
Prevention
The best way to prevent a bed bug infestation is to be vigilant. Inspect your home regularly for signs of bed bugs, such as small brown spots on mattresses and furniture. Vacuum your home frequently and wash bedding and clothing on a regular basis. If you travel, it’s important to inspect your luggage and clothing before bringing them into your home.
Extermination
If you discover a bed bug infestation, it’s important to take action immediately. The most effective way to get rid of bed bugs is to hire a professional exterminator. A professional exterminator will use a combination of chemical and non-chemical treatments to eliminate the bed bugs. This may include the use of insecticides, heat treatments, and steam treatments.
Conclusion
Bed bugs are notoriously difficult to control. The best way to manage a bed bug infestation is to use a combination of prevention and extermination methods. Prevention can help reduce the chances of an infestation, while professional extermination is the most effective way to get rid of bed bugs.
Bed Bug Prevention
- Check second-hand furniture and bedding before bringing it into the house.
- Vacuum regularly and throw away the bag after each use.
- Wash bedding, curtains and soft furnishings at high temperatures.
- Keep clothes off the floor and in sealed bags or containers.
- Use mattress, box spring and pillow encasements.
- Repair cracks in plaster and glue down peeling wallpaper.
- Remove clutter from bedrooms.
- Keep pets off the bed and furniture.
- Regularly inspect the bed and furniture for signs of bed bugs.
Bed bug prevention is the best way to avoid an infestation. Taking steps such as checking second-hand furniture and bedding before bringing it into the house, vacuuming regularly and throwing away the bag after each use, and washing bedding, curtains and soft furnishings at high temperatures can help reduce the likelihood of an infestation. Keeping clothes off the floor and in sealed bags or containers, using mattress, box spring and pillow encasements, repairing cracks in plaster and glue down peeling wallpaper, removing clutter from bedrooms, and keeping pets off the bed and furniture can also help. Finally, regularly inspecting the bed and furniture for signs of bed bugs is a key part of preventing an infestation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes bed bugs so difficult to kill?
Bed bugs are highly resilient pests that have developed numerous adaptations that make them difficult to eradicate. They have thin exoskeletons that make them resistant to many insecticides, and their small size allows them to hide in tiny crevices and cracks. Some bed bugs can even survive for several months without feeding and are able to tolerate a wide range of temperatures. Additionally, they can quickly develop resistance to insecticides that are used over long periods of time, making them difficult to control.
How can I prevent a bed bug infestation?
The best way to prevent a bed bug infestation is to be vigilant. Check second-hand furniture, clothing, and luggage for signs of bed bugs before bringing them into the home. Vacuum regularly, especially in areas where people frequently sit or sleep. Be sure to dispose of the vacuum bag immediately after vacuuming to avoid spreading bed bugs. Use mattress and box spring covers to reduce the risk of bed bugs nesting in these areas. Regularly inspect your bed for signs of bed bugs, such as dark spots or an unpleasant musty odor.
What are the most effective strategies for eradicating bed bugs?
The most effective strategies for eradicating bed bugs include using a combination of chemical and non-chemical treatments such as vacuuming, steam cleaning, encasing mattresses and box springs, discarding infested items, and applying residual pesticides. All of these control measures should be used in conjunction with one another to obtain the best results. Additionally, it is important to follow up with regular inspections and monitoring to ensure all bed bugs are eliminated.
What are the health risks associated with bed bug infestations?
Bed bug infestations can cause a variety of health risks, including skin rashes, allergies, and psychological effects. Bed bugs feed on human blood and can cause an allergic reaction in some people. They can also lead to secondary skin infections if scratched excessively. Bed bugs can cause psychological distress, such as anxiety and insomnia, due to the fear of being bitten. Additionally, bed bug infestations can lead to a decrease in quality of life due to the need to throw away infested items and the cost of pest control treatments.
Is there any way to predict when and where a bed bug infestation might occur?
Bed bug infestations can occur in any home, regardless of cleanliness, and can spread quickly. Factors such as location, clutter, and travel can increase the chances of bed bug infestations, but it is difficult to predict when and where an infestation may occur. Bed bugs are resilient and can travel easily, making it difficult to control their spread. Prevention measures such as regularly cleaning and vacuuming, inspecting second-hand furniture and clothing, and avoiding sharing bedding can help to reduce the risk of an infestation.
Conclusion
Bed bugs are a nuisance for many reasons. They are difficult to kill due to their hardy nature, which allows them to resist many of the common treatments used. They also reproduce quickly, making it difficult to eliminate them before they can reach a critical mass. Furthermore, they are also hard to detect, as they are small and can hide in many areas. However, with the right approach, it is possible to get rid of them and prevent them from returning.