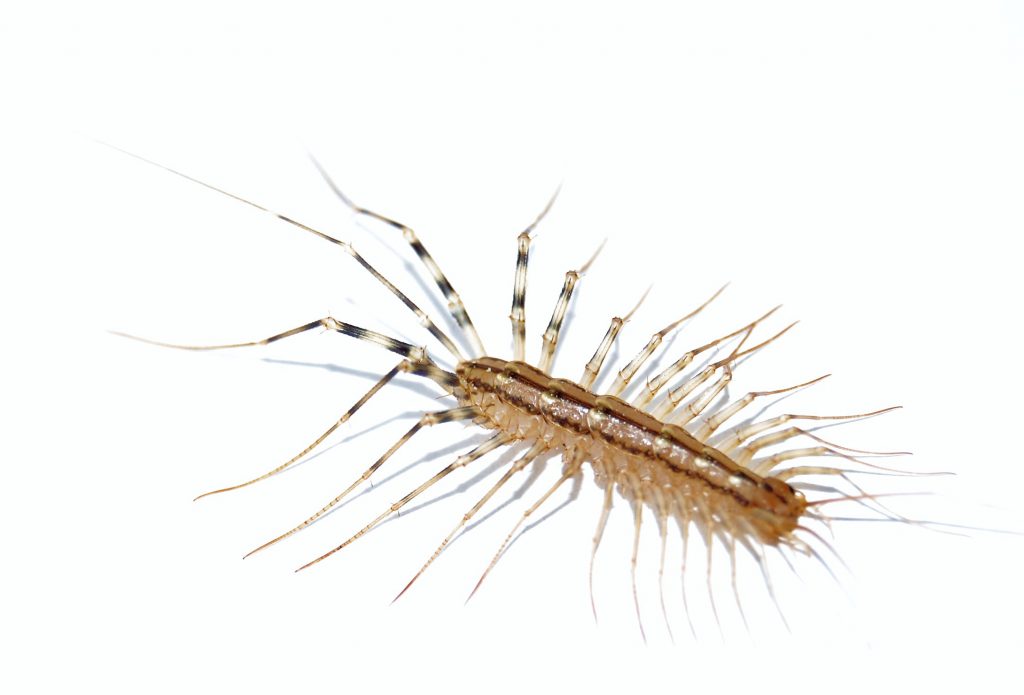
As a homeowner, one of the most frustrating pests to deal with are bed bugs. But what eats bed bugs? In this article, I’ll uncover the predators of this common bug and explain how you can use them to your advantage.
What are Bed Bugs?
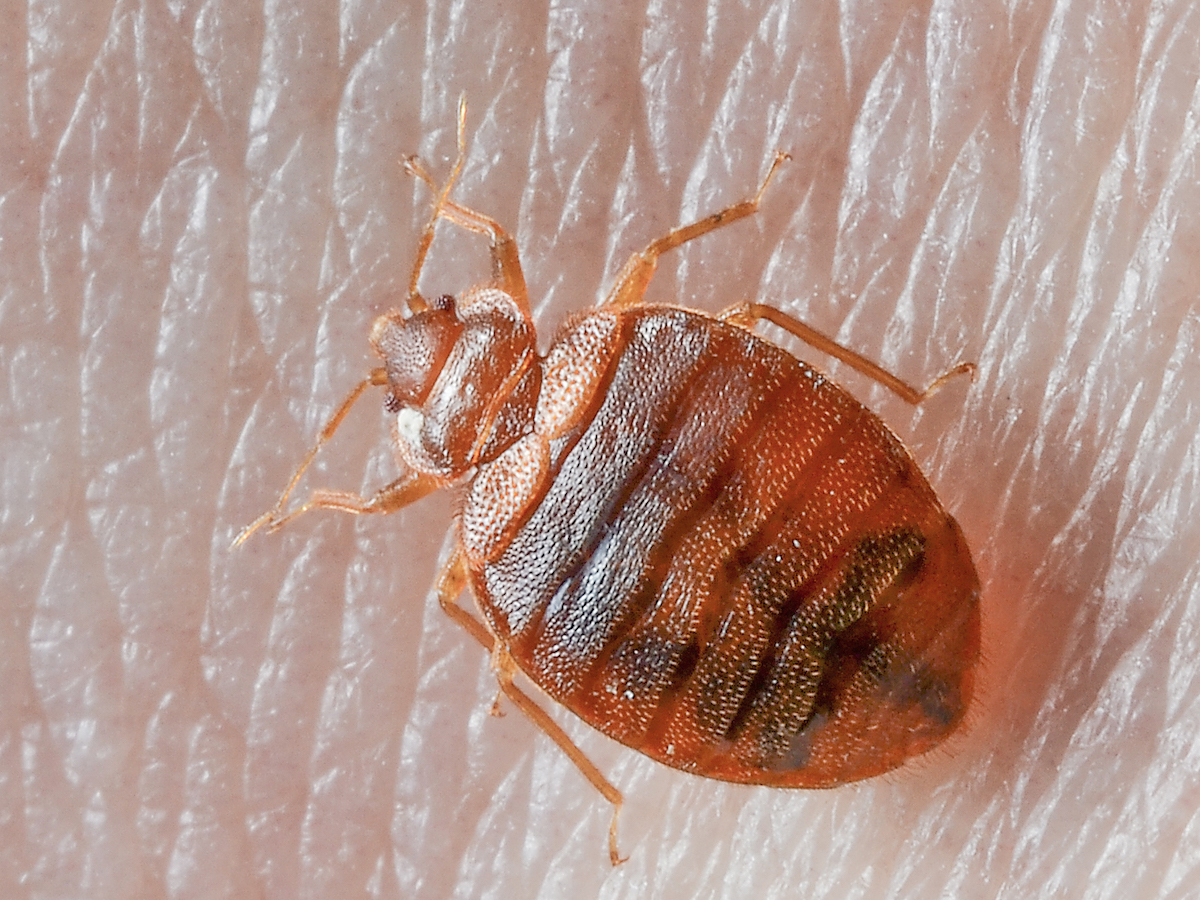

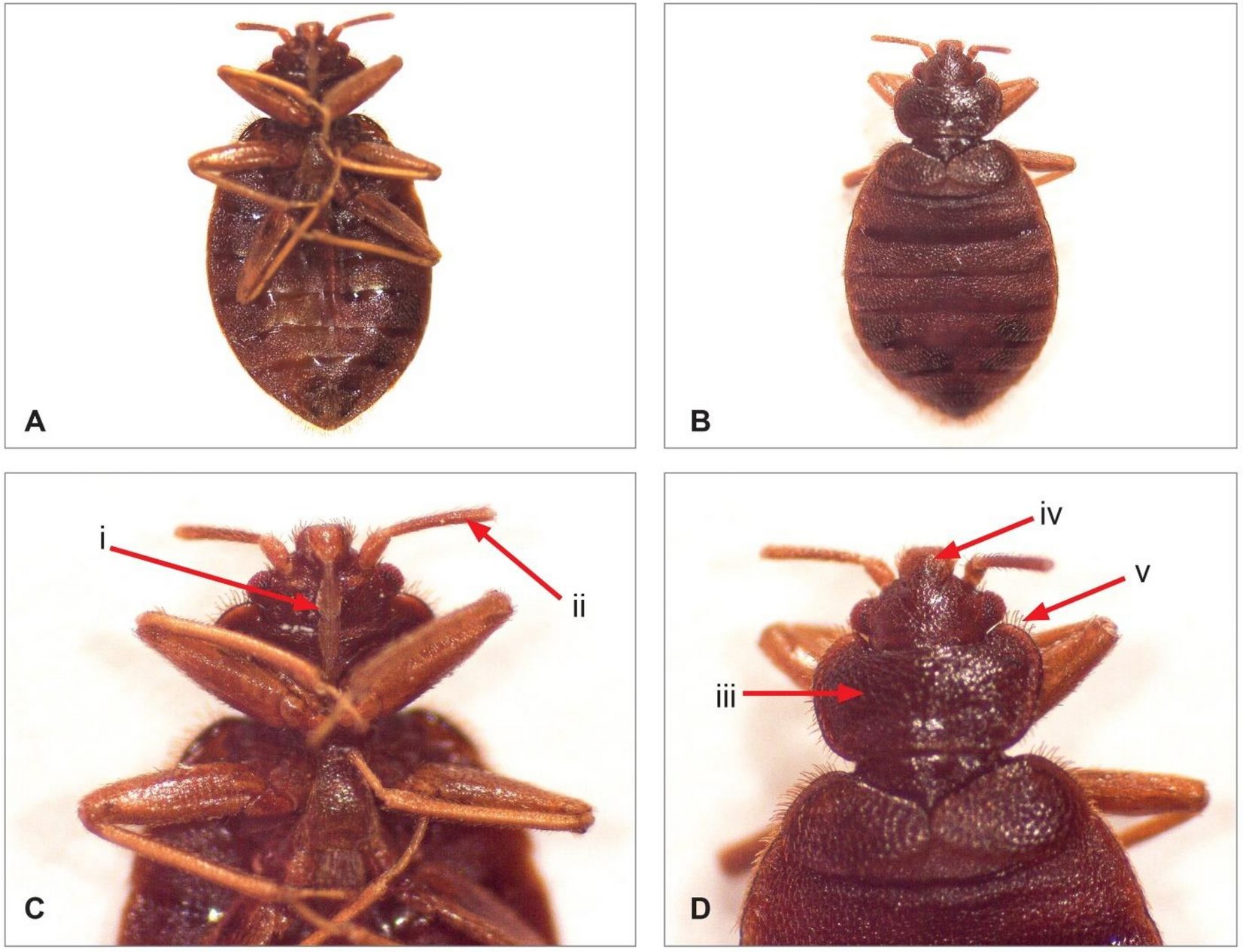
Bed bugs are small, parasitic, wingless insects that feed on human blood. They are usually found in beds, mattresses, and other areas where people sleep. Bed bugs are reddish-brown in color and can grow up to 6mm long. They are visible to the naked eye, but can be hard to spot due to their small size and ability to hide in tiny crevices.
Bed bugs tend to bite people at night while they are asleep, leaving itchy red bumps on the skin. Bed bugs can also spread skin infections and cause allergic reactions in some people.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Size | Can grow up to 6mm long |
| Color | Reddish-brown |
| Habitat | Beds, mattresses, and other sleeping areas |
| Feeding Habits | Feeds on human blood |
Predators of Bed Bugs

I’m looking for ways to get rid of bed bugs and it turns out there are a few natural predators that can help. Here are the top four creatures that eat bed bugs:
Insects
Many species of insects feed on bed bugs including certain species of beetles, wasps, and ants.
Arachnids
Spiders, mites, and ticks can all help to keep bed bug populations in check.
Lizards
Some species of lizards like geckos are known to feed on bed bugs.
Birds
Birds like swallows, starlings, and sparrows also feed on bed bugs.
Control of Bed Bugs

Natural Predators
I’ve heard that some bugs, such as spiders, centipedes, and carpet beetles, can eat bed bugs. But it’s important to understand that these natural predators usually don’t provide enough control to keep a bed bug infestation in check.
Chemical Control
The most effective way to get rid of bed bugs is to use chemical insecticides. These can be applied directly to the affected areas and provide quick results. There are several types of insecticides that can be used, including pyrethrins, pyrethroids, and neonicotinoids. It’s important to use the right type of insecticide for the situation and to follow the instructions on the label.
3. Non-Chemical Control

- Regularly vacuum the floors, carpets, upholstered furniture and mattresses.
- Encase mattresses and box springs in dust-proof or allergen impermeable covers.
- Reduce clutter in the residence, as bed bugs can hide in the crevices of such clutter.
- Wash and dry bedding, curtains, and clothing in hot water and high heat.
- Replace thin wall-to-wall carpeting with hardwood, tile, or linoleum floors.
- Discard infested items that cannot be washed or otherwise treated.
- Use high-powered fans to dry out areas that are prone to bed bug infestations.
- Check secondhand furniture prior to bringing it into the residence.
- Seal cracks and crevices with a caulking gun.
- Install door sweeps on exterior doors.
- Install window screens.
Impact of Bed Bugs on the Environment
Bed bugs are a nuisance to households and businesses, but they also have an impact on the environment. Here are some of the ways they can affect the environment:
- Bed bugs can spread pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and fungi, which can negatively impact the environment.
- Bed bugs can transfer from one place to another, which can lead to the spread of infestations.
- Bed bugs can reduce biodiversity by preying on native insects, which can disrupt the food chain.
- The chemicals used to kill bed bugs can contaminate the environment, including air, water, and soil.
- The presence of bed bugs can also lead to increased levels of stress in people, which can affect their physical and mental wellbeing.
Bed bugs are a nuisance to households and businesses, but they can also have a negative impact on the environment. It’s important to take the necessary steps to reduce the population of bed bugs, as well as to reduce their impact on the environment.
Benefits of Controlling Bed Bug Population
Controlling bed bug population offers numerous benefits:
- Reduction in the spread of disease: Bed bugs can carry and spread a range of diseases including typhus, salmonellosis, and plague.
- Reduction in allergies: Bed bugs can cause an allergic reaction in some people resulting in a range of symptoms including skin rashes, itchiness and respiratory problems.
- Reduction in discomfort and disruption: Bed bugs can be a source of considerable discomfort and disruption due to the bites they produce.
- Reduction in stress and anxiety: Bed bug infestations can be stressful and can cause a lot of anxiety in those affected.
- Reduction in property damage: Bed bugs can cause damage to property as they feed on wood, fabric and other materials.
Controlling bed bug populations is essential for the health, comfort and wellbeing of individuals, families and communities.
Potential Risks of Controlling Bed Bug Population
Controlling bed bug populations is a complex task, and there are a few potential risks associated with it. First and foremost, using chemical insecticides to kill bed bugs can have a number of health risks for humans and animals. These chemicals can be toxic if inhaled or ingested and can cause skin irritation or other health problems. Additionally, insecticides can also be hazardous to the environment, as they can contaminate the soil, water, and air.
Another risk associated with controlling bed bug populations is the possibility of introducing new pests into the environment. For example, if chemical insecticides are used to kill bed bugs, they might also kill beneficial insects, such as ladybugs, that prey on other pests. This can result in an increase in the population of other pests, such as aphids and other insects that can damage crops.
Finally, there is the risk of resistance. If bed bugs are repeatedly exposed to the same chemicals, they may become resistant to them, making them harder to control. This can result in an increase in the bed bug population and the need for stronger, more toxic chemical treatments.
| Potential Risk | Impact |
|---|---|
| Using chemical insecticides | Toxic to humans and animals, can contaminate environment |
| Introducing new pests | Can increase population of other pests, can damage crops |
| Resistance | Can result in an increase in the bed bug population and the need for stronger, more toxic chemical treatments |
In conclusion, controlling bed bug populations can be a difficult and potentially risky task, and it is important to understand the potential risks associated with it. When dealing with bed bugs, it is important to use safe, effective methods to ensure the safety of humans and the environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Predators of Bed Bugs?
Bed bugs have very few natural predators. The most common predators of bed bugs are spiders, mites, and some species of beetles. Other predators include centipedes, masked hunters, and some species of wasps. Some of these predators will actively hunt bed bugs, while others may simply eat them if they come across them while looking for other food sources.
How do spiders hunt bed bugs?
Spiders hunt bed bugs by using webs to capture them. The webs are usually located in dark places like cracks and crevices, where bed bugs are likely to hide. The web is designed to trap the bed bug, with the spider sensing the presence of the bed bug and then moving in to capture it. Spiders may also use pheromones to attract bed bugs to the web, making them easier to catch.
Are there any natural predators of bed bugs?
Bed bugs do not have any known natural predators in their environment, as they are adept at hiding from potential predators. There have been some studies on the potential of certain species of spiders, such as the Brown Recluse, to feed on bed bug eggs, but this has not been proven. Furthermore, bed bug eggs are covered in a protective coating, which makes them difficult for potential predators to penetrate.
What Role Do Ants Play in Controlling Bed Bugs?
Ants can be beneficial in controlling bed bug infestations, as they are natural predators of bed bugs. Ants are attracted to the sugary substance that is secreted by bed bug nymphs and adults. This sugary substance is referred to as “honeydew”. Ants will attack and feed on bed bugs, significantly reducing the population. Ants can be used as a natural form of pest control.
Are there any other insects that feed on bed bugs?
Yes, there are other insects that feed on bed bugs. These include ants, spiders, beetles, and earwigs. Some of these predatory insects, such as the spiders, can be found in the same areas as bed bugs. Other predators, such as earwigs, can be found in the same areas as bed bugs and can actively search for them. Ants, beetles, and spiders may also be attracted to bed bugs for the purpose of eating them.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bed bugs have a variety of predators that can help keep their populations in check. Natural predators like spiders, centipedes, and ants can help keep bed bug numbers down. Even other insects like silverfish, dust mites, and carpet beetles can help reduce the number of bed bugs in your home. To get rid of bed bugs, it’s best to contact a professional pest control service for the most comprehensive solution.







