As a homeowner, one of the last things you want to find out is that you have a bed bug infestation. But, how do bed bugs move around? In this article, we’ll explore the habits of these pesky creatures and uncover the mystery of how bed bugs move.
Bed Bug Biology
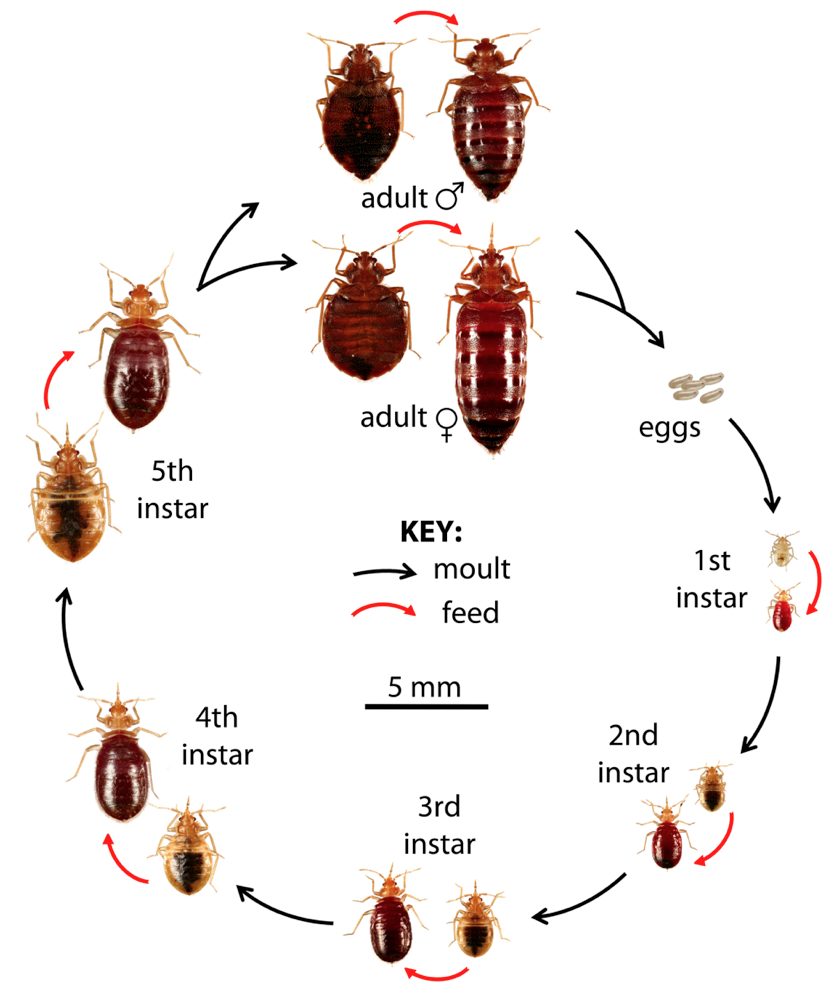
Bed bugs are small, flat, reddish-brown insects that feed solely on the blood of humans and other warm-blooded animals. Adult bed bugs are about the size of an apple seed and are about 3-4mm long. They have six legs and two antennae. Bed bugs have a segmented body with a head, thorax and abdomen. Their bodies are covered with a flexible cuticle and have hardened wing covers, although they do not fly.
Bed bugs have a specialized mouthpart called a stylet which is used to pierce the skin and suck blood. They have two compound eyes, but their vision is poor. Bed bugs have a pair of sensory antennae that help them to locate and recognize their hosts.
Bed bugs have a variety of survival adaptations that help them to feed, reproduce and move easily. They have a waxy coating on their body which helps them to maintain moisture. They can survive for long periods of time without feeding. They can also tolerate extreme temperatures, surviving in temperatures as low as 19°F and as high as 122°F.
| Characteristics | Details |
|---|---|
| Size | 3-4mm |
| Segmented Body | Head, thorax, abdomen |
| Mouthpart | Stylet |
| Eyes | Two compound eyes |
| Antennae | Two sensory antennae |
| Coating | Waxy coating |
| Temperature Tolerance | 19°F to 122°F |
Bed bugs are able to move quickly over many surfaces, including wood, fabric and walls. They can squeeze into the tiniest cracks and gaps, making it very hard to get rid of them once they have infested an area. They can also move from one location to another by hiding in people’s clothing, suitcases and other items.
Bed Bug Appearance
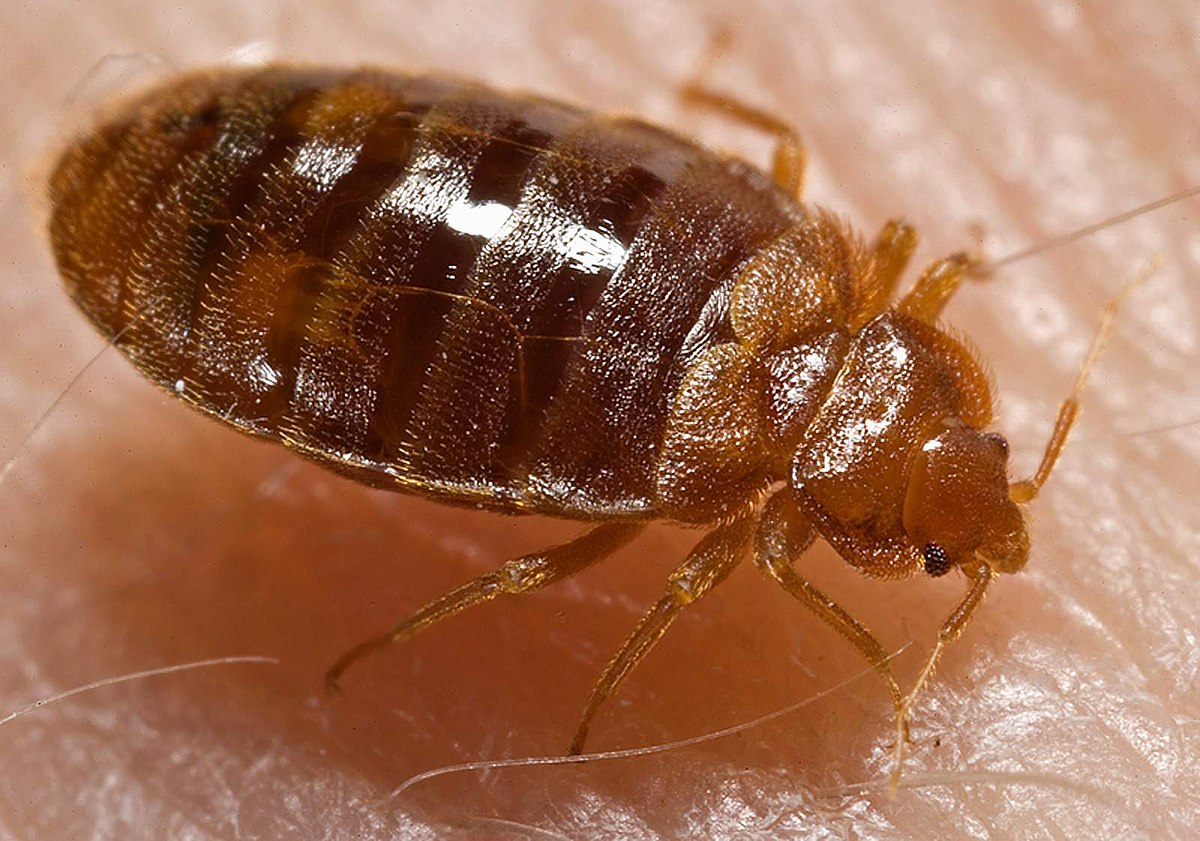

Bed bugs are small, flat, oval-shaped insects measuring around 5 to 7 millimeters in length. They are typically brown in color, but will turn reddish after they feed. Bed bugs have six legs, two antennae, and a segmented body. They have no wings, so they are not able to fly. A bed bug’s body is covered in short, fine hairs.
| Appearance | Description |
|---|---|
| Size | 5-7mm |
| Color | Brown-reddish |
| Legs | 6 |
| Antennae | 2 |
| Body | Segmented, covered in short, fine hairs |
Bed bugs have a flattened shape that allows them to hide in tight cracks and crevices. They are nocturnal, meaning they are most active at night while people are sleeping. Bed bugs are also attracted to body heat, carbon dioxide, and the scent of blood.
Bed Bug Behavior
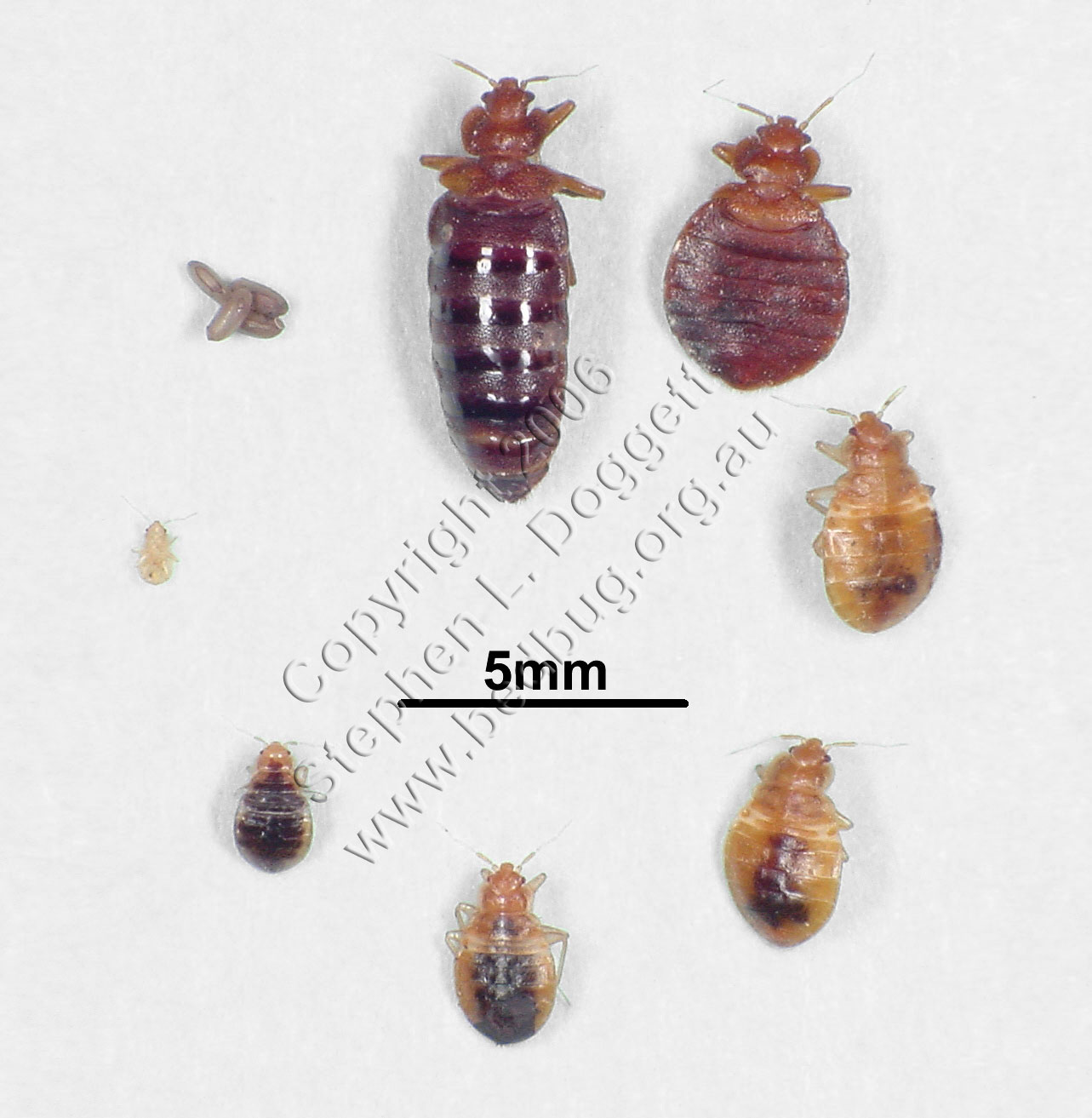

Bed bugs are nocturnal, meaning they are most active at night when humans are asleep. This is when they feed on their human hosts, as well as other warm-blooded animals like birds and bats. During the day, bed bugs will hide in areas such as mattress seams, box springs, headboards, and nearby furniture. They also hide in crevices in walls and floors, so they can be difficult to find.
Bed bugs are attracted to body heat, carbon dioxide, and sweat. They will travel up to 20 feet in search of a host, although they are most likely to stay within 8 feet of the bed. Bed bugs can also move between rooms and apartments through electrical outlets, pipes, and ventilation systems.
Bed bugs will feed for about five minutes, and then return to their hiding place. After a few days, they will come out again and feed. They can survive up to one year without feeding, so they can remain dormant for long periods of time.
Bed bugs are also highly resistant to many of the insecticides used to control other pests. That’s why it’s important to contact a professional exterminator if you suspect you have a bed bug problem.
How Bed Bugs Move
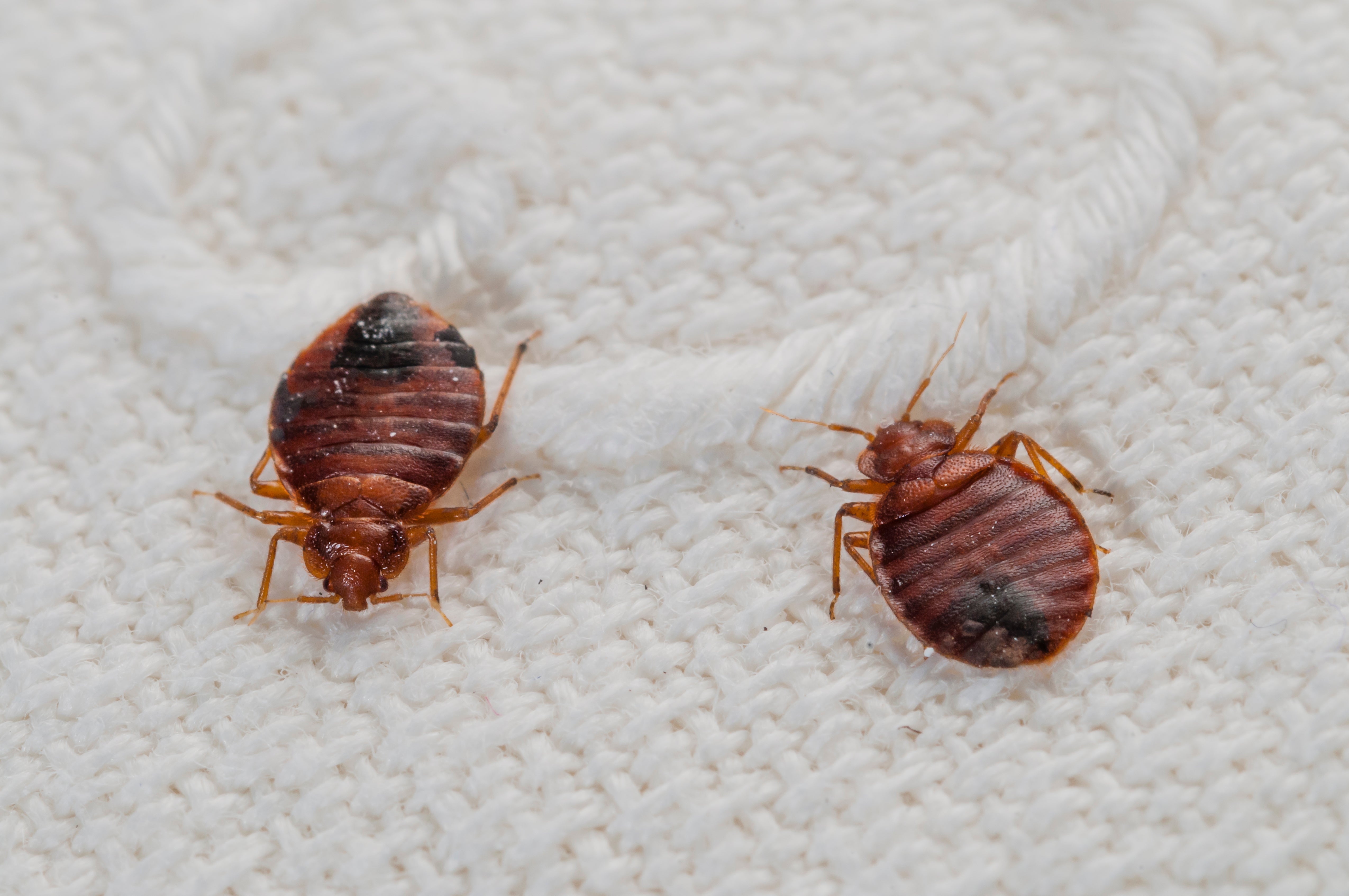

Bed bugs are notorious for their ability to move quickly and efficiently. Though they have no wings, they are able to climb walls and travel through cracks and crevices. They can move up to 3 feet per minute.
Bed bugs are able to walk, crawl, and climb. They can move on both flat or uneven surfaces. They often use their long front legs to climb up walls and ceilings. They can also use their claws to cling to rough surfaces.
Bed bugs can move horizontally as well. They can travel across floors and carpets, as well as through small cracks in walls. They are known to move quickly in order to search for a food source.
Bed bugs also have the ability to jump. They can jump up to 6 inches high and up to 8 inches horizontally. This is a useful ability for them to move from their hiding place to a new host.
| Movement | Speed (approx) |
|---|---|
| Walk/Crawl | 3 ft/min |
| Climb | – |
| Jump | up to 8 in. horizontally |
Bed bugs are also able to fly. Though they do not have wings, they are able to use the wind to move from one place to another. This is a useful ability for them to move from their hiding place to a new host.
Bed bugs are incredibly mobile creatures, and they are able to move quickly and efficiently. With their ability to climb, walk, crawl, and jump, they can travel great distances and find a new host.
How Bed Bugs Travel from Room to Room

Bed bugs are highly mobile and can move from room to room with ease. They can travel:
- Through cracks in walls and floors
- Through furniture, especially beds and couches
- Through electrical outlets and wiring
- Through vents and ducts
- Through clothing, bedding, and other fabrics
- Through luggage and other items being transported from one place to another
Bed bugs can also travel on their own, although they tend to avoid light and prefer to move around in the dark. They are able to crawl across a room in a relatively short amount of time. They can also move quickly between floors and can even climb up or down walls.
Since bed bugs can move so easily, it is important to be aware of their potential presence in any room. If you suspect that bed bugs may be present, it is important to take action to prevent them from spreading to other rooms. This may include vacuuming, steam cleaning, and other preventive measures.
How Fast Bed Bugs Move from Room to Room
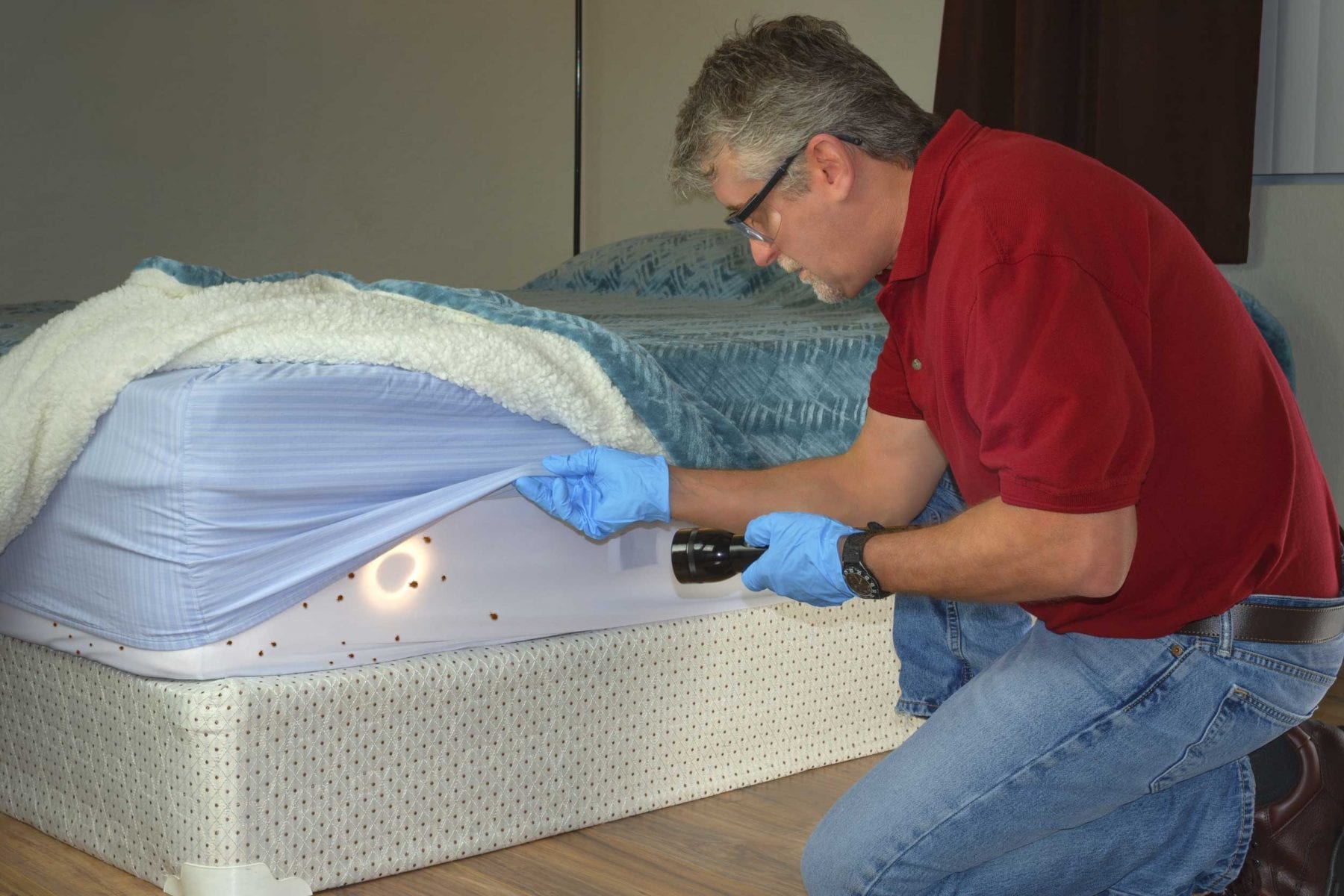

Bed bugs have evolved over time to become one of the most efficient home invaders. They can move quickly and easily from room to room, and even from one unit to another in a multi-unit building.
Bed bugs are capable of moving up to 20 feet in a single night and can cover up to 100 feet in a week. This means that they are capable of moving from one room to another within a matter of hours. They can even move between floors in multi-unit buildings by using pipes, electrical wiring, and other crevices.
Bed bugs move by crawling and can travel up to 100 feet in a single night. This means that they can travel from one room to another within an hour or two and can spread quickly throughout an entire building.
Table:
| Mode of Transportation | Distance | Time |
|---|---|---|
| Crawling | 100 feet | 1-2 hours |
| Pipes/Wiring | Multi-floor buildings | N/A |
Bed bugs are extremely efficient at moving between rooms and can spread quickly. By understanding how quickly bed bugs can move from room to room, you can better prepare yourself for an infestation.
Bed Bug Control
Bed bugs are difficult to control as they can spread quickly, so it is important to act quickly to prevent an infestation. The most effective way to control bed bugs is to use a combination of chemical and non-chemical methods. Chemical treatments for bed bugs include using insecticides to kill bed bugs and their eggs. These treatments must be applied by a professional pest control operator using an approved insecticide. Non-chemical treatments include heat treatments, vacuuming, steam cleaning and freezing. Heat treatments involve raising the temperature of an infested area to a level that is lethal to bed bugs. Vacuuming is an effective way of removing bed bugs and their eggs. Steam cleaning is also effective in killing bed bugs, but the steam must reach a temperature of at least 120°F to be effective. Freezing is also an effective method of killing bed bugs, but the temperature must be below 0°F to be effective.
Prevention
Bed bugs are hard to control and can spread quickly through a home or hotel. To prevent a bed bug infestation, I recommend the following:
- Regularly inspect bedding, mattresses, and furniture for signs of bed bugs.
- Vacuum carpets and upholstered furniture.
- Eliminate clutter where bed bugs can hide.
- Regularly inspect and clean behind and underneath furniture.
- Check for bed bugs when traveling and when staying in a hotel.
- Keep suitcases away from furniture and bedding.
- Be aware of second-hand furniture and clothing.
- Seal cracks and crevices in walls and floors.
- Use mattress and box spring covers.
If I suspect a bed bug infestation, I should contact a pest control professional. A professional can inspect the premises and determine the best treatment plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do Bed Bugs Move from One Location to Another?
Bed bugs can move from one location to another in a variety of ways including through luggage, clothing, furniture, and even through small cracks and crevices. As they are small and lightweight, they can easily travel to other locations. Bed bugs are also able to move quickly and can travel up to 20 feet in a single night. Additionally, bed bugs can survive for long periods of time without food and can live up to a year without feeding.
How far can bed bugs travel in a single night?
Bed bugs are extremely mobile and can travel relatively long distances in a single night. Depending on the conditions, they can travel up to 20 feet in a single night. This makes it easy for them to spread from room to room or even from one apartment to another.
What Factors Influence Bed Bug Movement?
Bed bug movement is affected by a variety of factors, such as temperature, humidity, food sources, and the availability of hiding places. Temperature and humidity levels that are too high or too low can cause bed bugs to become inactive. Bed bugs are also attracted to certain odors, such as those from humans, and can be drawn to a particular location by the presence of an odor. Bed bugs also need a food source to survive, and they will travel to areas where they can find a food source, such as humans or other warm-blooded animals. Lastly, bed bugs need places to hide, and they prefer dark, secluded areas such as cracks and crevices.
How do Bed Bugs Travel from Room to Room?
Bed bugs can travel between rooms easily by crawling along baseboards and other surfaces. They can hide in furniture, clothing, and other items, making it easy for them to hitch a ride and be transferred from one room to another. They can also travel through air ducts and vents, allowing them to spread quickly throughout a home or building. Bed bugs can also be brought into a home from the outside, on items like clothing, luggage, or furniture.
How Fast Do Bed Bugs Move From Room To Room?
Bed bugs can move quickly and can travel up to 20 feet in a single night, though they typically stay within 8 feet of a human host. Once they have established a presence in a room, they can spread to other areas within a home or building. Bed bugs can also move through walls and floors. They can also be transported on clothing and furniture, on luggage, and via other people or animals.
Conclusion
Bed bugs have been one of the most infamous and persistent pests for centuries, and understanding their behavior has been a challenge for pest control experts. The research into their habits has revealed that bed bugs are incredibly mobile and can quickly move from one area to another. They have adapted to a wide range of host behaviors and environments, and their ability to survive in harsh conditions has allowed them to spread rapidly. Furthermore, they are able to survive long periods of time with no food, and can even go dormant for extended periods of time. To effectively control bed bug populations, it is important to understand their movements, behaviors, and the conditions that attract them. With the right knowledge and pest control strategies, bed bug infestations can be eliminated.
- Goddard, J., & deShazo, R. (2014). Bed Bugs (Cimex lectularius) and Clinical Consequences of Their Bites. JAMA Dermatology, 150(12), 1368–1373.
- Yoon, K. S., Kim, J. H., Lee, J. H., & Lee, S. H. (2017). Characteristics of Bed Bug (Hemiptera: Cimicidae) Movement. Journal of Medical Entomology, 54(3), 662–669.






